Keywords: Near-Infrared Spectrometer, Miniature Fiber Optic Spectrometer, Grains and Legumes, Agricultural Applications, Non-Destructive Testing
Background
Agriculture is one of the earliest fields to apply near-infrared (NIR) detection technology, primarily for measuring the content of various components in agricultural products. Compared to other methods, NIR Spectrometer saves a significant amount of time. Agricultural workers initially used NIR Spectrometer to measure the moisture content of agricultural products. Since then, it has been applied to qualitative and quantitative measurement of various substances and their intrinsic components with good results. NIR Spectrometer has advantages such as convenience, speed, low cost, non-destructiveness, and non-pollution. Compared to traditional detection methods, non-destructive testing does not damage the tested object, allows testing of the entire sample to avoid incomplete sampling, and offers fast testing speeds.
Principle of Near-Infrared Spectrometer
NIR spectrometers utilize the characteristics of the near-infrared region, quantifying features such as absorption, reflection, and scattering of light to obtain the spectral information of the sample. NIR refers to electromagnetic waves with wavelengths between visible light and mid-infrared light, ranging from 780 to 2500 nm, which are absorption spectra of molecular vibration overtones and combination frequencies. It primarily involves the absorption of hydrogen-containing groups (C-H, O-H, N-H, S-H). The absorption coefficient is small, the spectral bands are wide, irregularly shaped, and severely overlap. These broad peaks are related to the chemical composition of the sample.
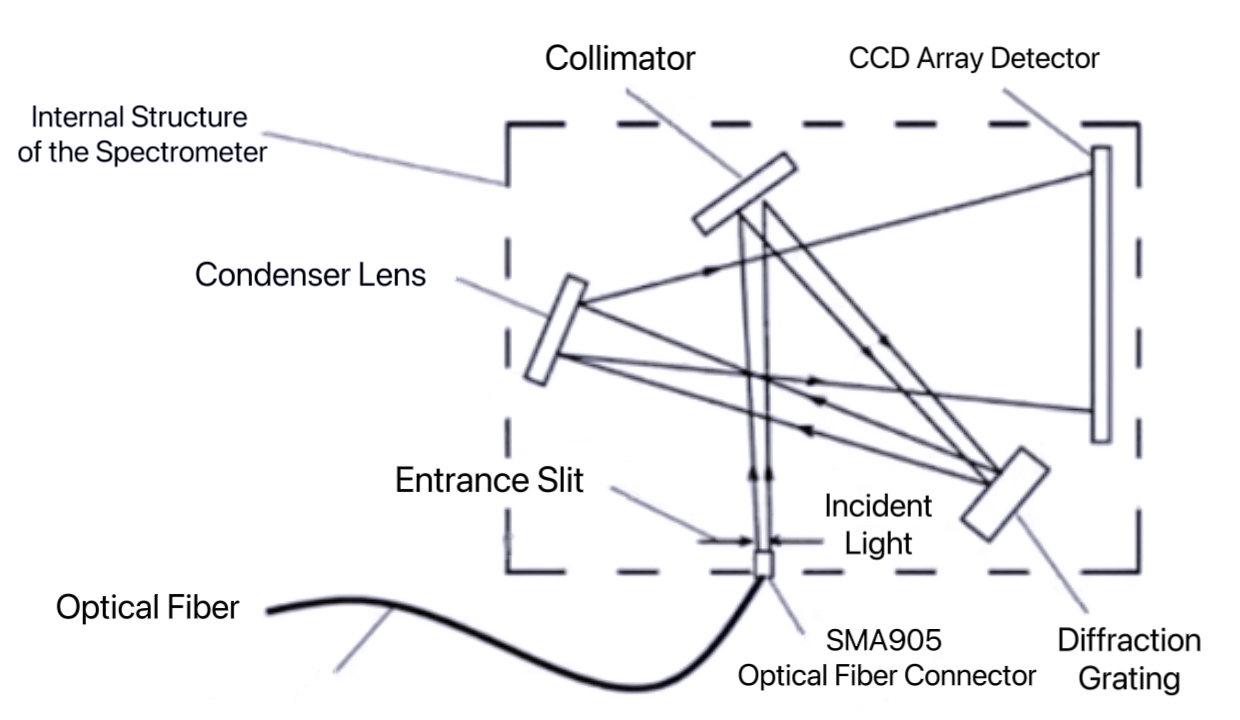
Spectrometer
To achieve quality testing of grains and legumes (such as moisture content, protein content, and oil content), component analysis (such as the content of carbohydrates, cellulose, and mineral elements in grains and legumes), and rapid screening, JianZhi Technology has developed a reflective NIR spectrometer. This system consists of modules such as a light source, a dispersing system, a grating, CCD signal acquisition, and computer control. It enables rapid measurement of NIR spectral data of samples, meeting the basic requirements for on-site sample quality analysis.
Selection and Advantages of Spectrometers
Fourier-transform infrared spectrometers, while highly precise, are not suitable for portable and online NIR detection applications due to their large size and high cost. Miniature fiber NIR spectrometers offer numerous advantages, such as small size, lightweight, structural stability, high cost-effectiveness, fast analysis speed, and high efficiency, making them very suitable for portable and online applications.
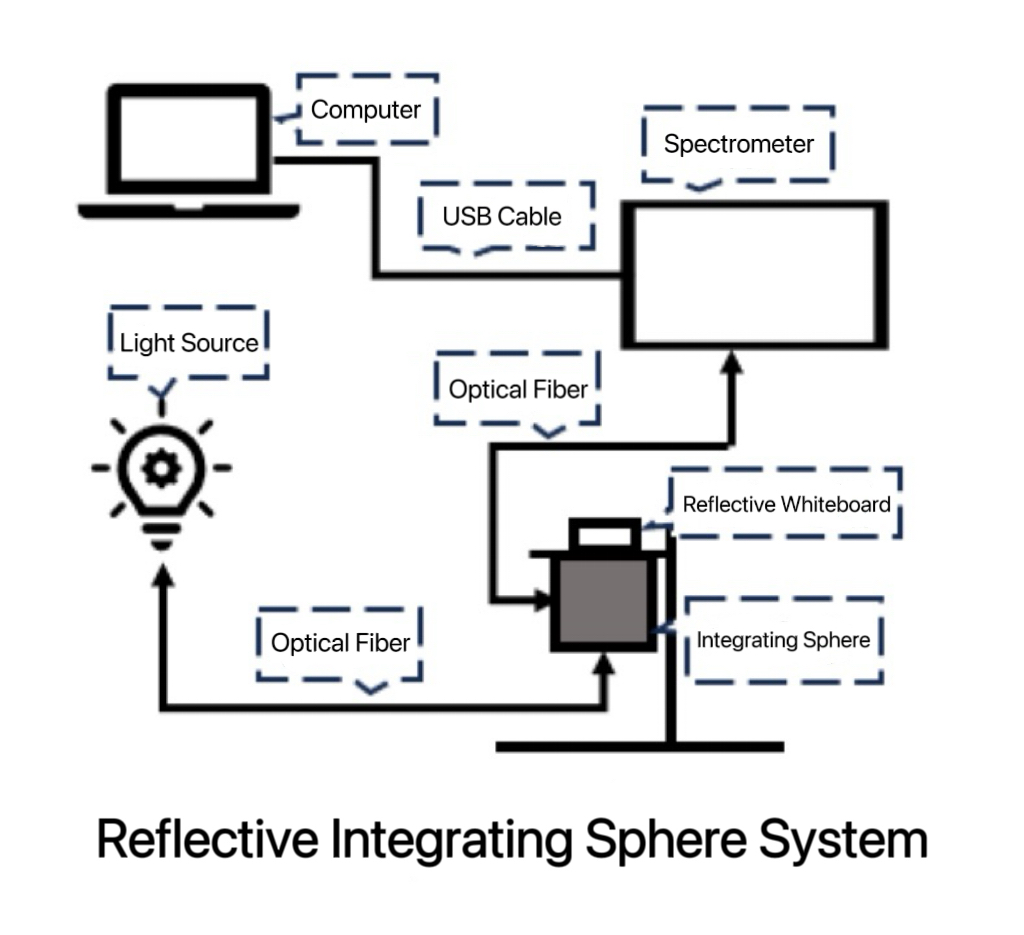
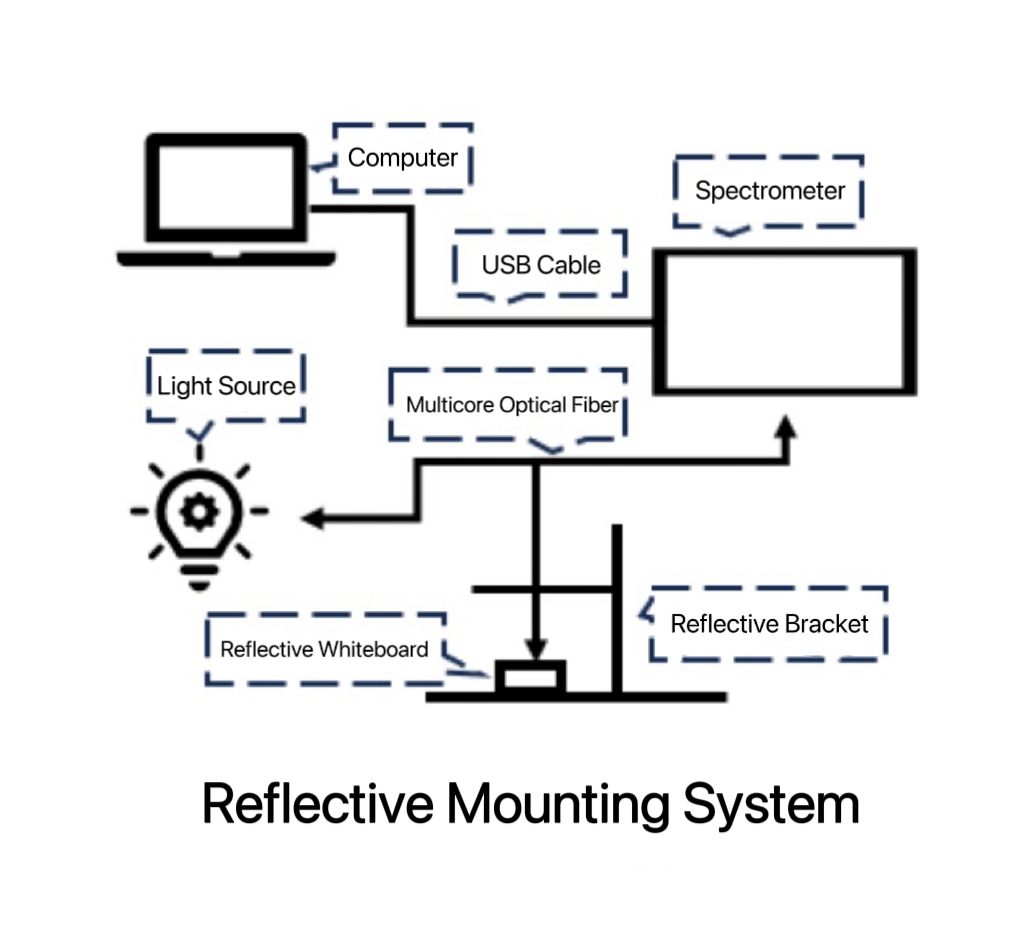
Experimental System Setup
As shown in the figure above, the setup requires a near-infrared light source, optical fibers, the JINSP SR50R17 near-infrared spectrometer, a reflection stand or integrating sphere, and a white reflection board. This setup is suitable for testing most raw and powdered samples of grains and legumes.
Recommended Spectrometer
The JINSP SR50R17 is a highly recommended and cost-effective near-infrared spectrometer. It has a wavelength range of 900 nm to 1700 nm, covering a wide range of conventional near-infrared detection areas. It uses an uncooled InGaAs sensor, which has high sensitivity. The lenses have high near-infrared reflection efficiency, allowing the detection of weak absorption signals. Its high resolution enables better discrimination of characteristic peaks. The spectrometer is compact, making it easy to set up in experiments and integrate into complete systems. It offers various data acquisition methods and is compatible with USB or UART output modes. For more details, please visit the website: Best SR50R17 Near Infrared Non-cooled Spectrometer manufacturers and suppliers | JINSP (jinsptech.com)
Post time: May-30-2024