Water pollution is a serious environmental problem, which brings great influence to people's production and life. The atmospheric pressure cathode Atomic emission spectroscopy (ELCAD-AES) system is an important device for detecting heavy metal content in water, and the spectrometer also plays an indispensable role in the device. The following introduces a method for detecting heavy metal content in water using atomic emission spectroscopy, taking lead as an example.
1. Measurement principle
The device uses a flowing liquid as the discharge cathode and a metal rod as the discharge anode, and the gas between the two poles is broken down under the action of high voltage, resulting in atmospheric glow discharge plasma. The type and concentration information of metal elements in the water can be obtained by detecting the spectrum of the plasma with a spectrometer.
2. Test equipment and conditions
The atmospheric pressure liquid cathode glow discharge device is shown in the figure. The discharge anode is a tungsten rod with an elliptical lower end. The liquid to be tested enters the conical glass capillary tube under the guidance of the peristaltic pump. The inflowing liquid is the discharge cathode. The solution overflows from the upper end of the conical glass capillary and enters the solution tank. A metal auxiliary electrode is connected to the solution tank, and the auxiliary electrode is connected to the stainless steel electrode connected to the negative pole of the power supply. In the atmospheric environment, the optical signal received by the optical fiber is transmitted to the spectrometer and then displayed and processed by the computer.
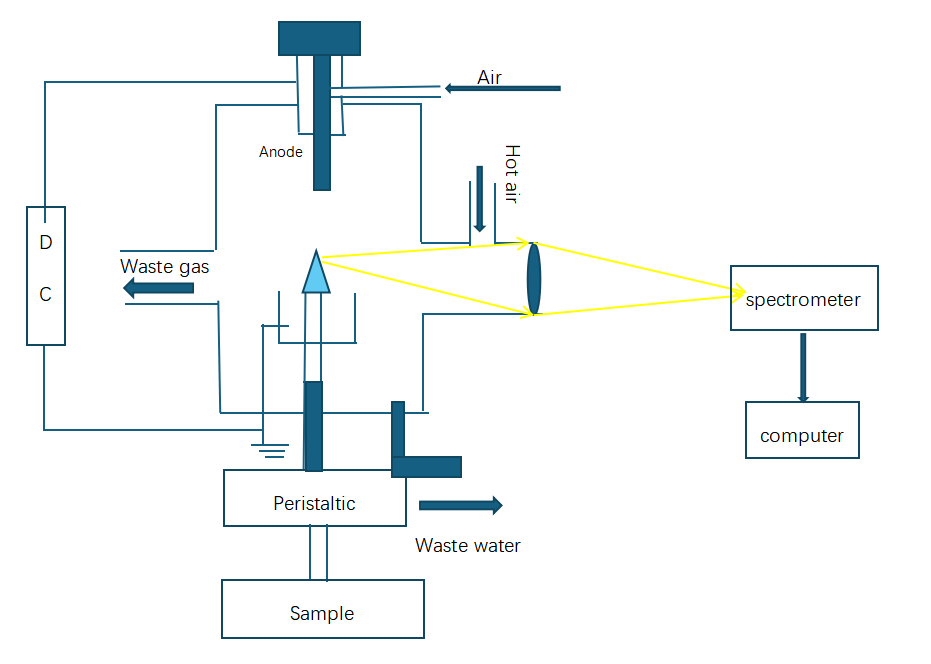
( Equipment and reagents: adjustable high-voltage DC power supply; peristaltic pump; spectrometer, SR50C spectrometer of JINSP is recommended, HNO3, HCL, H2SO4, Pb(NO3)2 )
3. Spectral analysis
The basis for spectral quantitative analysis comes from the formula:
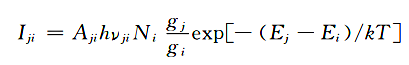
Among them, Aji is the transition probability, hυji is the energy of the radiated photon, g is the statistical weight, Ei and Ej are the excitation energies of the j-level and i-level peristaltic pump sample exhaust gas DC power supply hot air air anode waste liquid spectrometer computer. From this formula, it can be seen that the spectral line intensity and the excitation potential are in a negative exponential relationship. The excitation potential of Pb is higher, so the spectral line intensity is weaker. The spectral line intensity is proportional to the ground state atoms, and the number of ground state atoms is proportional to the element concentration. Therefore, under certain conditions, the spectral line intensity is proportional to the element concentration.
The emission lines in the nitrated lead nitrate solution include the molecular lines of OH and N2, the atomic lines of Na, K, Hα, Hβ, and O, and the atomic lines of Pb, which are 368.35nm and 405.78nm. Due to the interference of the N2 molecular line near 368.35nm, 405.78nm is selected as the experimental analysis line. After obtaining the spectrum, the lead content in the water can be obtained by comparing the data. The same method can also be used to detect the content of heavy metals such as copper and mercury in water.
The spectrometer used in the experiment is recommended to be SR50C from JINSP. If necessary, please click the link below to enter the official website of JINSP: Best SR50C miniature spectrometer manufacturers and suppliers | JINSP (jinsptech.com)
Post time: Jul-25-2024

