Keywords: Diabetes, Non-invasive Blood Glucose, Raman Spectroscopy, Transcutaneous Detection, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease with a rising incidence globally, significantly impacting patients' quality of life and placing a burden on healthcare resources. Blood glucose monitoring is crucial for the prevention and management of diabetes and its complications. However, current methods such as home-use fingertip blood glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors can be painful and inconvenient. Non-invasive blood glucose detection technology can effectively address these issues, playing an essential role in diabetes prevention and treatment.
Among non-invasive blood glucose detection technologies, Raman spectroscopy has garnered considerable attention in recent years due to its potential. Jinsp has conducted preliminary experimental research on non-invasive blood glucose detection based on recent advancements in Raman spectroscopy, achieving breakthrough results.
High-Efficiency Spatial Raman Spectroscopy System: Overcoming Skin Fluorescence Interference
Dr. Wang Chengming's team at Jinsp Technology designed and built a high-throughput Raman spectroscopy system based on Jinsp's transmission spectrometer to address the issue of high skin fluorescence interference. This efficient Raman spectroscopy system was successfully used for quantitative glucose detection in tissue fluid simulants—bovine serum solutions.
Experimental results indicated that distinct glucose Raman characteristic peaks at 1060 cm-1 and 1125 cm-1 could be directly observed in the Raman spectra of bovine serum with different glucose concentrations. The peak intensity showed a good linear relationship with glucose concentration (R2 = 0.998), confirming the system's capability for quantitative glucose concentration detection in tissue fluids.
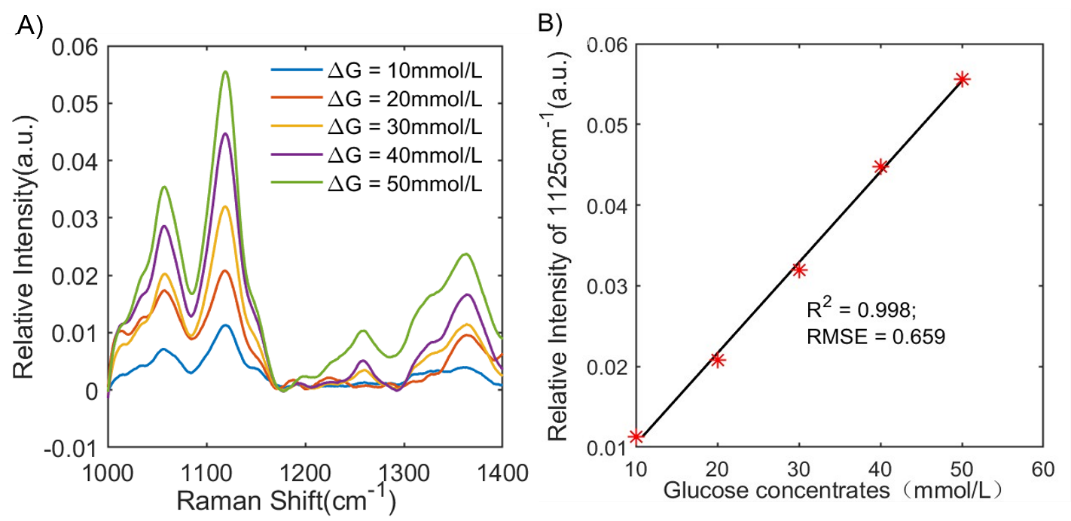
Figure 1: A) Differential Raman spectra of glucose in bovine serum simulants,
B) Standard curve of glucose concentration in bovine serum simulants.
OCT Technology: Precise Localization for Transcutaneous Measurements
To further explore the feasibility of transcutaneous non-invasive blood glucose detection using Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution imaging of the skin structure and capillary network distribution in vivo was performed using Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). The matched transcutaneous measurement sites were analyzed. By comparing the Raman spectra of palm skin areas with significant differences in blood glucose concentration, the glucose characteristic peak at 1125 cm-1 was directly detected under conditions of significant blood glucose concentration differences, similar to the results from the bovine serum experiment. This finding provides direct evidence for the feasibility of transcutaneous non-invasive blood glucose detection using Raman spectroscopy.
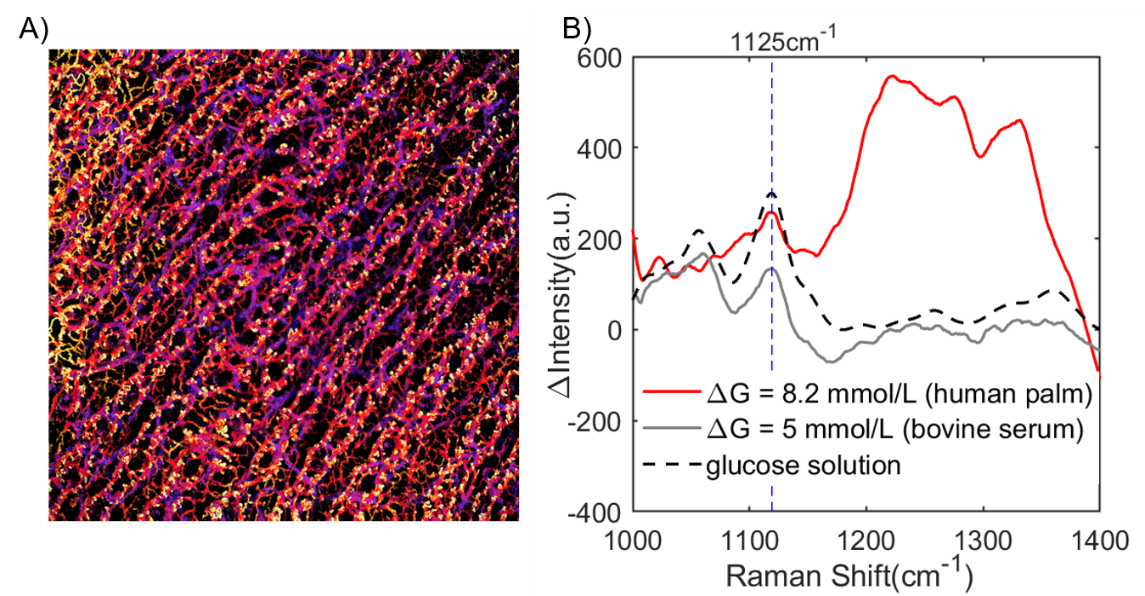
Figure 2: A) Capillary network distribution in the superficial dermis of palm skin imaged by OCT,
B) Direct observation of glucose characteristic peak signal in transcutaneous Raman spectra of the palm.
Transmission Spectrometer: Key Equipment for Raman Spectroscopy
The transmission spectrometer is a critical component of the Raman spectroscopy system in non-invasive blood glucose detection. It separates the collected sample Raman scattering signals by wavelength. The separated light signals are projected onto a detector, which converts these light signals into electrical signals. By analyzing these electrical signals, detailed information about the spectrum, such as peak position and intensity, can be obtained. This information is used to infer the molecular structure and composition of the sample. Therefore, the performance of the transmission spectrometer directly affects the quality of the Raman spectra and, consequently, the accuracy of blood glucose concentration detection. Jinsp's high-throughput transmission fiber optic spectrometer, equipped with VPH transmission gratings, achieves nearly 90% diffraction efficiency and features an optical design with excellent imaging performance. Its sensitivity can be up to five times that of reflective spectrometers and can achieve twice the resolution limit of traditional spectrometers. Additionally, it is equipped with a research-grade deep-cooled area array CCD camera with very high quantum efficiency and signal-to-noise ratio. These characteristics of high sensitivity and high resolution provide reliable data for the observation and quantitative analysis of glucose Raman characteristic peaks.
For details on the transmission spectrometer, see OCT - JINSP Company Limited (jinsptech.com)
The research results from Jinsp provide a new solution for non-invasive blood glucose detection technology, greatly facilitating daily monitoring and management for diabetes patients. With continuous improvement and optimization, non-invasive blood glucose detection technology is expected to play a more significant role in clinical applications in the future.
Jinsp is a professional company focused on spectroscopy detection technology, originating from Tsinghua University. They provide comprehensive and reliable spectroscopy analysis solutions to customers. Their mature products include near-infrared spectrometers, miniature fiber optic spectrometers, transmission spectrometers, high-sensitivity fiber optic spectrometers, and OCT spectrometers.
Post time: Jun-25-2024

